Torrent Browser User Interface Guide
Torrent Suite Software space on Ion Community
BaseCaller Parameters
This page describes BaseCaller parameters that are available when you reanalyze a completed run.
Changes in the 4.4 release
Barcode filtering
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| barcode-filter-named | Off | The default in Torrent Suite 4.4 is that all barcodes in which the user specified a sample name are represented in the run report. If you want barcodes with an associated sample name to go through the barcode filtering process (as in Torrent Suite 4.2 and earlier), turn this option on. |
| barcode-ignore-flows | 0,0 | Two comma separated integer values specify an open-ended interval of flows that are ignored during barcode classification. If lower and upper bound are equal, no flows will be ignored. |
Barcode classification
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| barcode-auto-config | Off |
The classification algorithm computes the minimum Hamming distance of the barcode set in flow space and attempts to choose appropriate barcode-cutoff and barcode-separation settings.
The components of 'barcode-auto-config' can be activated separately:
The command line option 'barcode-check-limits on' (in combination with 'barcode-compute-dmin on') results in sanity checks of the cutoff and barcode-separation option values. Should an option value be out of bounds, it is changed to the value that auto-config would choose.
The bounds for 'barcode-check-limits' are:
|
Changes in the 4.2 release
Barcode classification method
The barcode classification method that is used in the Torrent Suite Software analysis pipeline is changed beginning with the 4.2 release. Barcodes now are classified based on signal information rather than on base call information, as was done in 4.0 and previous releases. S ignal calls are a more direct measurement of the read and are the most precise and most accurate source of information. The 4.2 barcode classification method considers the distance between the measured signal and the predicted barcode signal. The 4.0 method considered the number of flow alignment errors in base space.
Advantages of the 4.2 classification method:
- Because this method uses a barcode separation threshold that is based on signal information, it provides increased confidence in the identification and rejection of reads. Using signal information, the BaseCaller can detect problematic reads that in base space appear to perfectly match a barcode.
- The consistency and uniformity of barcode classification is improved. The 4.0 classification method constantly adjusted the classification threshold. In 4.2, the threshold is a defined percentage of the most frequently-occurring barcode (1%, by default).
BaseCaller parameters
The settings of BaseCaller parameters control barcode classification, and these parameters have also changed in the 4.2 release:
-
--barcode-mode2 is the default in 4.2. This setting causes the 4.2 barcode classification behavior. -
The
parameter
--barcode-cutoff, has a different meaning than in 4.0. In 4.2,--barcode-cutoffsets the maximum allowed squared distance ( between the measured signal and the predicted barcode signal) .
These new parameters are added in the 4.2 release:
-
--barcode-separationis minimum separation between the best and second best barcode choice to assign a read to a barcode . -
--barcode-postpone, when set to the 4.2 default of 1, postpones most barcode filtering until after an Ion Proton run's 96 blocks are merged into one. (Some low level pre-filtering still happens at the block level to reduce the number of files that need to be transferred and merged.) Final b arcode filtering is done on the chip's full information as a whole, not on a block-by-block basis.
Note: As always, the 4.2 defaults for these parameters are optimized for the barcode set IonXpress.
Barcode classification for Ion Proton analyses
For Ion Proton sequencing runs, the chip is logically divided into 96 blocks. For signal processing and base calling stages of the analysis pipeline, the data from each block is analyzed independently from other blocks and also from the chip's data as a whole.
4.0
In the 4.0 release, barcode classification and also barcode filtering are done independently in each block. A barcode is reported in the run report if it passes barcode filters in any block. With this approach, noise in a single block can cause an unused barcode to erroneously appear in the run report. Noise could be from various issues such as a loading problem in a small area of the chip or a small bubble in the flow. The edges of bubbles are especially associated with error spikes that cause barcode classification errors in the 4.0 release a single noisy block can cause phantom barcodes to be reported (erroneously) as present in the analysis.
Also in the 4.0 release, reads that fail barcode filtering are filtered out and are not reported in the BAM file or in other files. These reads are silently rejected and cannot be inspected for troubleshooting or other reasons.
4.2
In the 4.2 release, barcode filtering is performed considering all the chip's data as a whole. B arcode filtering is postponed until after the data from all 96 blocks of the chip are merged. We see that this approach avoids many of the phantom barcode issues that are seen in 4.0 due to noise in one of the 96 blocks.
To approximate the 4.0 classification behavior in the 4.2 release
Use the following parameter settings to have the 4.2 release approximate the 4.0 barcode classification behavior:
-
--barcode-mode1 -
--barcode-cutoff2
Due to changes in the behavior of base calibrationand also in the internal quality tables, the 4.2 release cannot exactly reproduce the 4.0 barcode classification behavior.
Basic parameters
This table lists the more common BaseCaller parameters.
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| --barcode-cutoff |
1.0 (Float) |
Maximum distance allowed in barcode matches. A threshold that sets the stringency for barcode matches. Lower values require more exact matches when assigning reads to barcodes. Higher values allow less exact matches. Reads that have a distance greater than this value are counted as barcode no-matches. See also The cutoff setting . |
| --barcode-mode |
2 (Integer) |
Allowed values: 1, 2
Note: --barcode-mode 0 is no longer supported. |
| --barcode-separation |
2.5 ( Float ) |
This setting controls how much ambiguity in barcode assignment you want to tolerate, by
investigating the distances to the both the closest barcode and to the next closest barcode. A read is rejected if the difference in these two distances is less than the
Note:
See also The separation setting . |
| --barcode-postpone | 1 |
Allowed values: 0, 1, 2
Note: We do not recommend that you change this parameter. Instead accept the pipeline defaults (which are different for Ion S5, Ion PGM, and Ion Proton analyses). |
| --barcode-filter |
0.01 (Float) |
Barcode frequency threshold to be reported in the UI.
Set to 0.0 to turn this filter off. The setting 0.0 causes all barcodes in the barcode set to be reported in the UI, including barcodes with no or very few reads, provided that the barcode group has at least
|
| --barcode-filter-minreads |
20 (INT) |
Threshold for the minimum number of reads in a barcode group, for that group to be reported in the UI. . |
The cutoff setting
Notes about the
--barcode-cutoff
parameter with
--barcode-mode
1:
-
0 is the most restrictive setting.
--barcode-cutoff0 allows only reads that perfectly match a barcode in base space.
-
The setting 0 works with any barcode set (both Ion Torrent sets and custom barcode sets).
-
Do not set
--barcode-cutoffgreater than 2 with the IonXpress barcode set. Values greater than 2 relax the classification rules and allow incorrect barcode assignments.
A rule of thumb for the maximum
--barcode-cutoff
setting is based on the minimum distance of the barcode set in flow space:
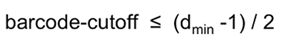
T
he minimum distance f
or the IonXpress barcode set is 5. Then the maximum recommended value for
--barcode-cutoff
is 2 for analyses that use
the IonXpress barcode set. (See
Custom Barcode Design
for more information about minimum distances within a barcode set.)
The separation setting
Notes
about the
--barcode-separation
parameter:
-
Larger values (close to the minimum distance of the code) require more strict matching of the predicted signal for a read to be assigned to a barcode.
-
Smaller values (for example, 0.2 and below) allow barcode assignment with an expanded tolerance for errors. For example in the extreme case of separation=0, the measured signal may be right in between two predicted barcode signals.
-
If
--barcode-separationis set at or above the minimum distance of the barcodes in flow space, no reads at all are assigned to a barcode. -
If
--barcode-separationis set close to the minimum distance of the barcodes in flow space, very few reads are assigned to a barcode. -
If
--barcode-separationis too small, the risk of cross contamination increases. More ambiguous reads are forced into a barcode assignment (with a higher rate of error in these assignments).
A rule of thumb for a good
--barcode-separation
setting is one half of the minimum distance of the barcode set in flow space:

Other public parameters
This table lists the public BaseCaller parameters that are available for you to modify. However, please note that the defaults for these parameters are optimized for most scenarios and in most cases the default settings are recommended.
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
-d, or --disable-all-filters |
off |
When on, disables all filtering and trimming and overrides other filtering and trimming settings.
|
|
-k, or --keypass-filter |
on | When on, filters out reads that do not both produce a signal and match the library key (or the test fragment key). |
| --min-read-length |
25 (Int) |
F ilters out reads less than this minimum read length.
This filter screens out poor reads early on to avoid wasting processing time on them. See also
|
|
--extra-trim-left
|
0 (Int) |
Trims this number of bases beyond the barcode adapter. |
| --trim-adapter-cutoff |
16 ( Float ) |
A score cutoff value. Smaller values correspond to more stringent adapter search and larger values to less stringent adapter search. Set to 0 to turn off. |
| --trim-adapter-min-match |
6 ( Int ) |
The minimum number of P1 adapter bases required in order to trim the P1 adapter. |
| --trim-qual-window-size |
30 ( Int ) |
Window size for quality trimming. |
| --trim-qual-cutoff |
16 ( Float ) |
Cutoff for quality trimming. Set to 100 to turn off. When set to 100, no reads are filtered out due to this parameter. |
| --trim-min-read-len |
25 ( Int ) |
F ilters out any reads that fall below this minimum read length after any trimming step. By default it is initialized with the value of 'min-read-length'. |
BaseCaller filters
The BaseCaller module and its parameter settings control these types of filtering:
- Keypass
- Quality trimming
- Adapter trimming
(For a conceptual overview of the BacseCaller's trimming, see Overview of BaseCaller and Barcode Classification . For a detailed discussion, see Technical Note - Filtering and Trimming .)
Examples of BaseCaller parameters usage
With these examples:
- Do not remove the string "BaseCaller" from the Basecaller Args field.
- Do not change BaseCaller parameters other than those listed in the basic table or the public table (unless specifically directed to do so by Ion).
Turn off all filtering and trimming
Use the
parameter
--disable-all-filters
on
to turn off all filtering. Here is an example Basecaller Args field:

Note: Your analysis most probably contains other parameters in the Basecaller Args field. Do not remove or modify the other parameters.
The
--disable-all-filters
on
setting overrides other filter settings.
Turn off keypass filtering
Use the parameter
--keypass-filter off
to turn off keypass filtering. Here is an example Basecaller Args field:

Turn off quality filtering
Use the parameter
--trim-qual-cutoff
100
to turn off quality filtering. Here is an example Basecaller Args field:

Note: Your analysis most probably contains other parameters in the Basecaller Args field. Do not remove or modify the other parameters.
Turn off adapter filtering
Use the
parameter
--
trim-adapter-cutoff
0
to turn off adapter filtering. Here is an example Basecaller Args field:

Note: Your analysis most probably contains other parameters in the Basecaller Args field. Do not remove or modify the other parameters.
Assign more reads to barcodes
To assign more reads to barcodes, adjust barcode classification settings towards less stringent settings:
-
Increase the
--
barcode-cutoffsetting -
Decrease the
--
barcode-separationsetting.
Do not filter out any barcodes
Use the
--barcode-filter=0.0
with
--barcode-filter
-minreads
0.0
to show all barcode read groups where at least one read is classified as belonging to this barcode group.

Other BaseCaller and barcode classification pages
Other resources in Torrent Suite Software user documentation:
- BaseCaller Parameters (including changes in the 4.2 release)
- Troubleshooting Barcode Classification Issues
- Custom Barcode Design
- Filtering and Trimming Tech Note
 Torrent Browser User Interface Guide
Torrent Browser User Interface Guide
 The Login Page
The Login Page
 The Plan Tab
The Plan Tab
 Templates
Templates
 Planned Runs
Planned Runs
 Plan by Sample Set
Plan by Sample Set
 Create Samples and a Sample Set
Create Samples and a Sample Set
 Sample Attributes
Sample Attributes
 Template and Planned Run Wizard
Template and Planned Run Wizard
 Create Multiple Run Plans
Create Multiple Run Plans
 Create a Template with Ion AmpliSeq.com Import
Create a Template with Ion AmpliSeq.com Import
 The Monitor Tab
The Monitor Tab
 The Data Tab
The Data Tab
 Completed Runs and Reports Tab
Completed Runs and Reports Tab
 Work with Completed Runs
Work with Completed Runs
 Reanalyze a Completed Run
Reanalyze a Completed Run
 BaseCaller Parameters
BaseCaller Parameters
 TMAP Parameters
TMAP Parameters
 The Projects Listing Page
The Projects Listing Page
 Project Result Sets Page
Project Result Sets Page
 Compare Multiple Run Reports
Compare Multiple Run Reports
 CSV Metrics File Format
CSV Metrics File Format

